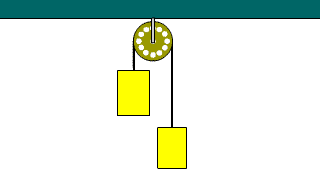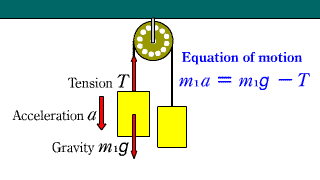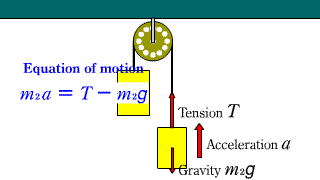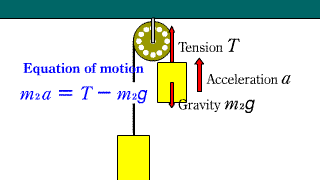|
 |
|
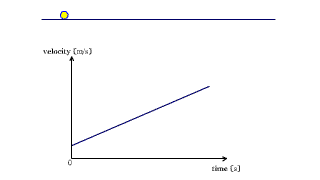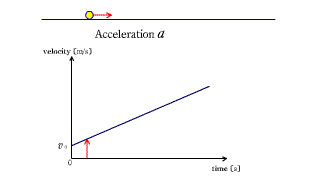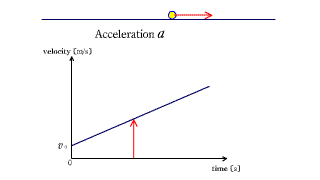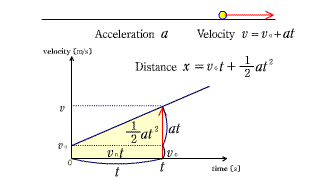
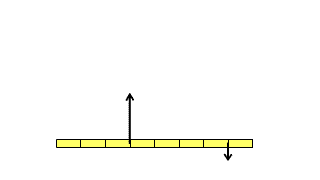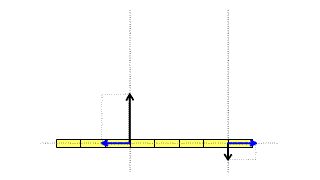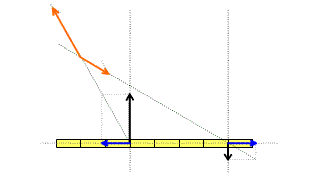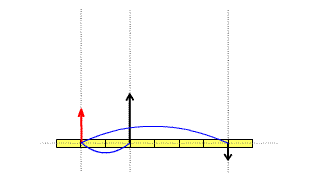
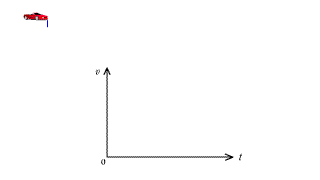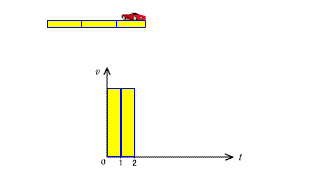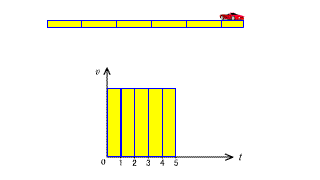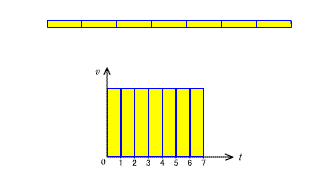
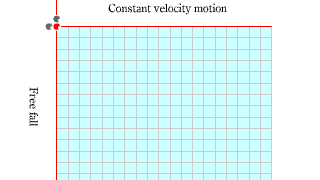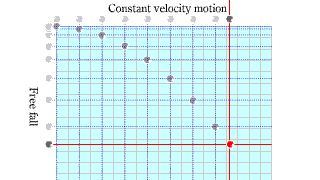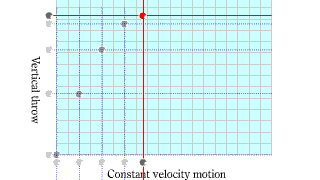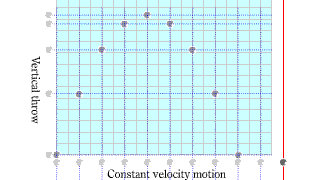
| The area of the v-t graph in constant velocity motion represents the distance. |
|
|
 |
|
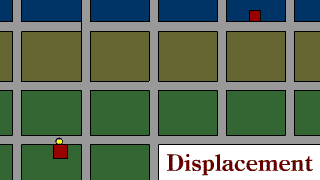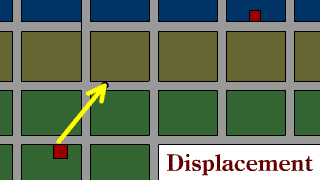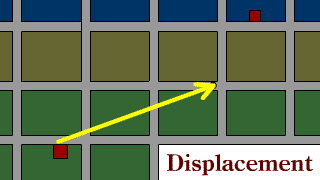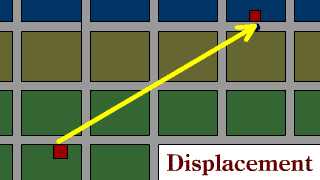
| Displacement is the direction from the start point and how much the position has changed over a straight line distance. |
|
|
 |
|
When a boat travels over a river that moves like a conveyor belt, the speed of the river is added.
|
|
|
 |
|
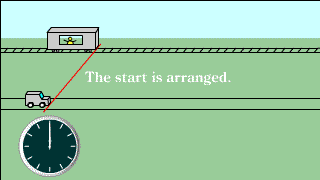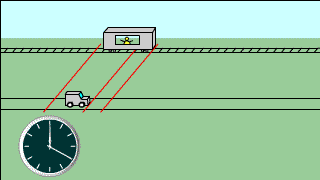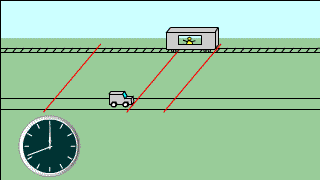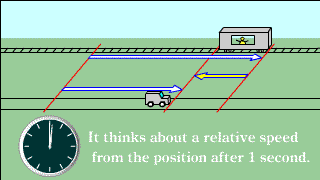
| The position of an object as seen by a moving observer is the relative velocity in which direction and how far away it is per unit time. |
|
|
 |
|
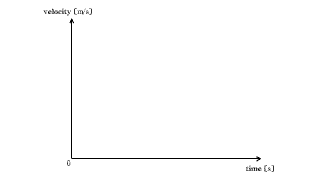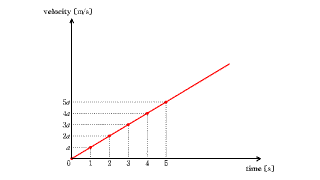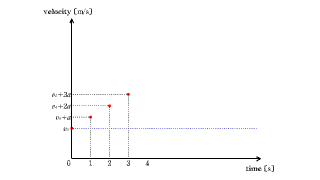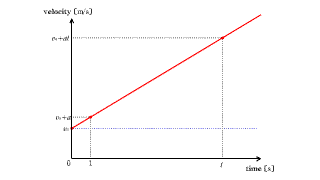
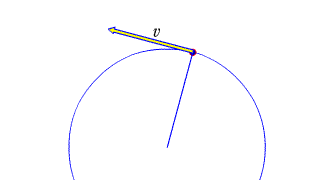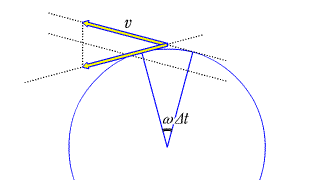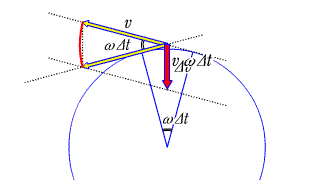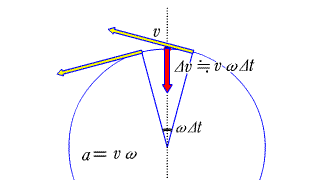
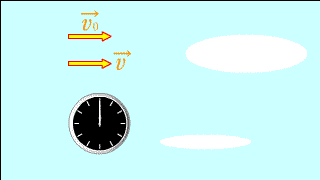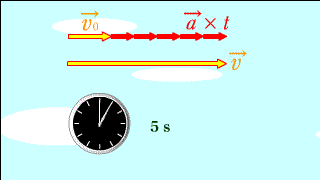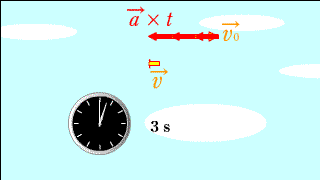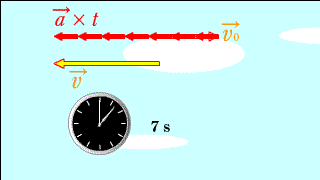
Each red arrow represents acceleration.
The changing yellow arrow below indicates the speed at that time. |
|
|
 |
|
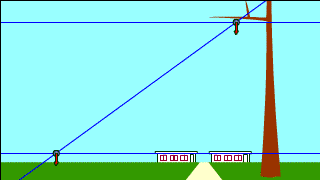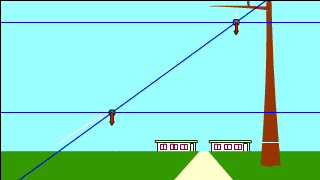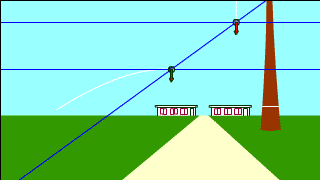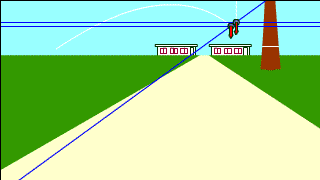
| Whenever a free-falling object and a projectile-motion object aiming at it are launched at the same time, they collide. |
|
|
|
|
 Parabola movement Parabola movement |
 |
|
| The motion of a horizontally projected / obliquely projected object is explained separately for the horizontal component and the vertical component. |
|
 Action and reaction Action and reaction |
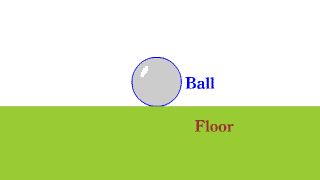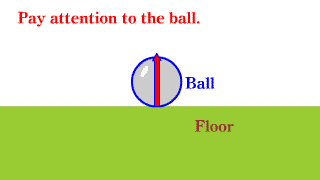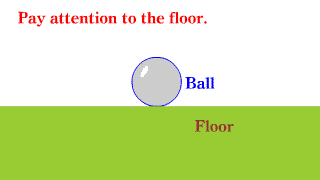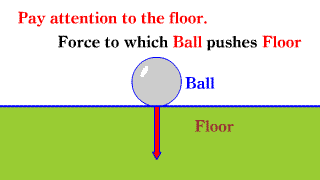 |
|
| It is necessary to keep in mind that the force of action / reaction is the force acting on different objects. |
|
 Frictional force Frictional force |
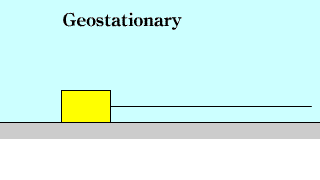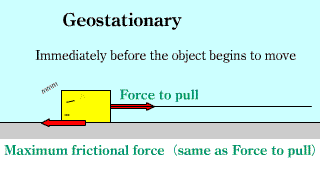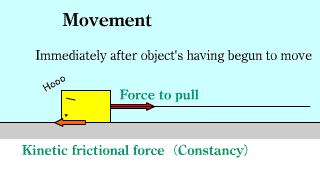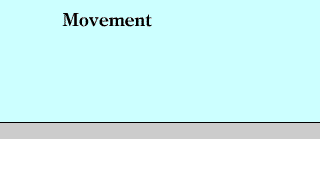 |
|
| The static friction force and the maximum friction force are the same as the force acting on the object, and the dynamic friction force is constant. |
|
 Pully Pully |
 |
|
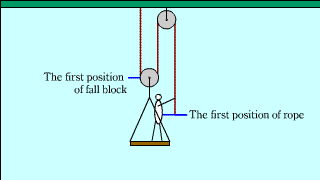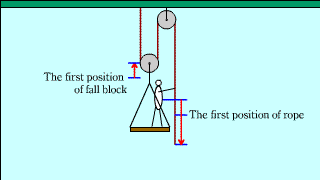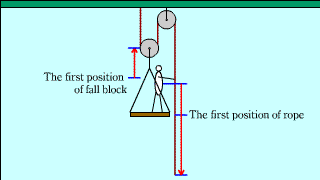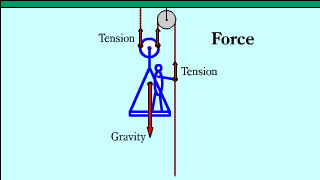
| The explanation that the pulling force when you lift yourself on a moving pulley is one-third is suppressed by two, "the principle of work" and "the force acting on an object". |
|
 Bounce of spin Bounce of spin |
 |
|
| When a topspin or backspin ball bounces, the ball receives frictional force from the floor and bounces differently. |
|
 Magnus effect Magnus effect |
 |
|
| When air sticks to a spinning ball, Bernoulli's theorem creates a difference in air pressure, which exerts force on the ball. |
|
 Laws of motion Laws of motion |
 |
|
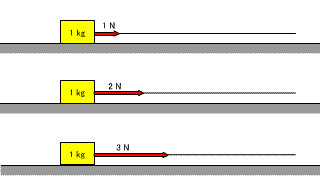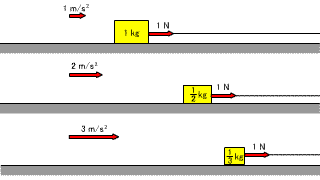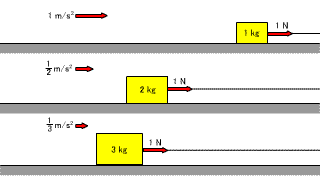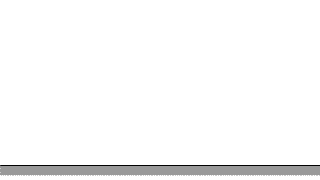
| If the mass of the object remains the same and the magnitude of the force applied to the object is changed, the magnitude of the acceleration generated in the object also changes. |
|
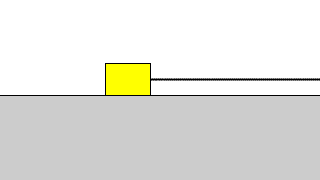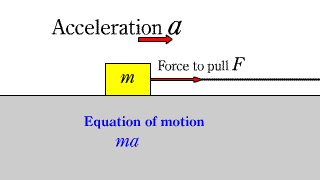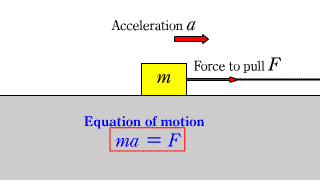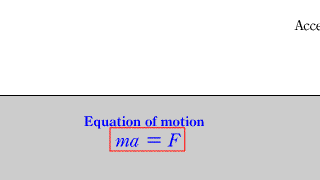
 Motion equation 1 Motion equation 1 |
 |
|
| When a horizontal force acts on an object on a horizontal floor without friction, the equation of motion for the object is established. |
|
 Motion equation 2 Motion equation 2 |
 |
|
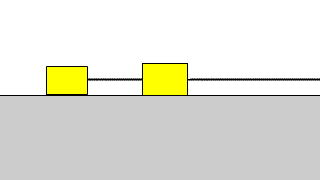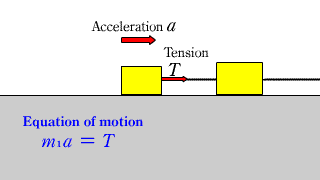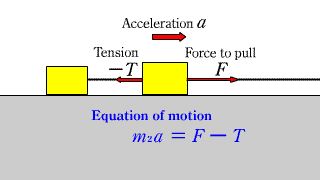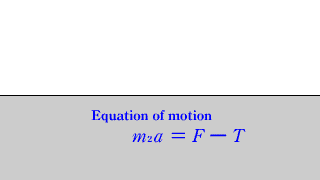
| When a horizontal force acts on two objects connected by a string on a horizontal floor without friction, the equation of motion for each object is established. |
|
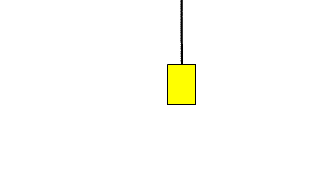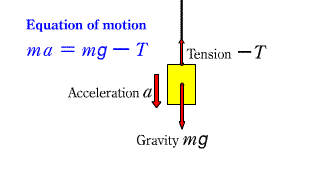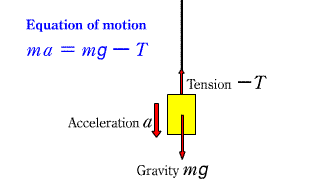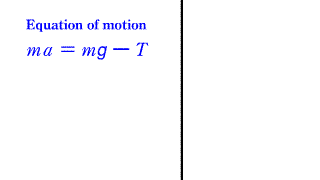
 Motion equation 3 Motion equation 3 |
 |
|
| This is the equation of motion when an object suspended by a string falls down. |
|
 Motion equation 4 Motion equation 4 |
 |
|
| When another object is hanging through a pulley on a stringed object on a horizontal floor without friction, the equation of motion for each object is established. |
|
 Atwood_Machine Atwood_Machine |
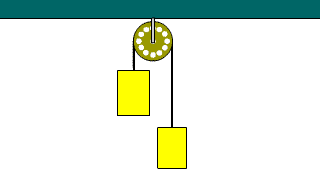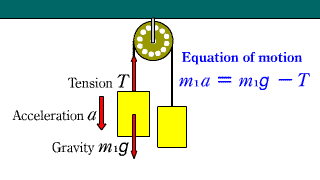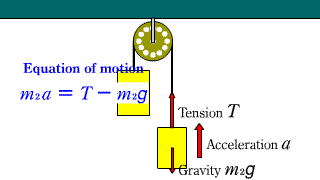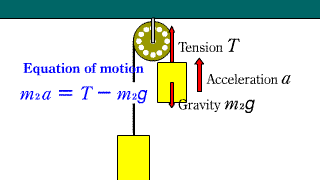 |
|
When two objects connected by a string are hanging through a fixed pulley, the equation of motion for each object is established.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
 Movement of center of gravity Movement of center of gravity |
 |
HTML5 Canvas |
| This is the movement of the center of gravity of an object that is undergoing simple vibration or rotational movement. |
|
|
|
|
|